
Again, depletion and enhancement mode transistors are further classified into respective N–Channel and P–Channel. MOSFETs are classified into Depletion Mode and Enhancement Mode. Junction FET transistors are further classified into N–Channel JFET and P–Channel JFET depending on their construction. The FET transistors are classified into JFET and MOSFET. The BJTs are again classified into NPN and PNP transistors. They are: Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) and Field Effect Transistors (FET). Transistors are basically classified into two types.

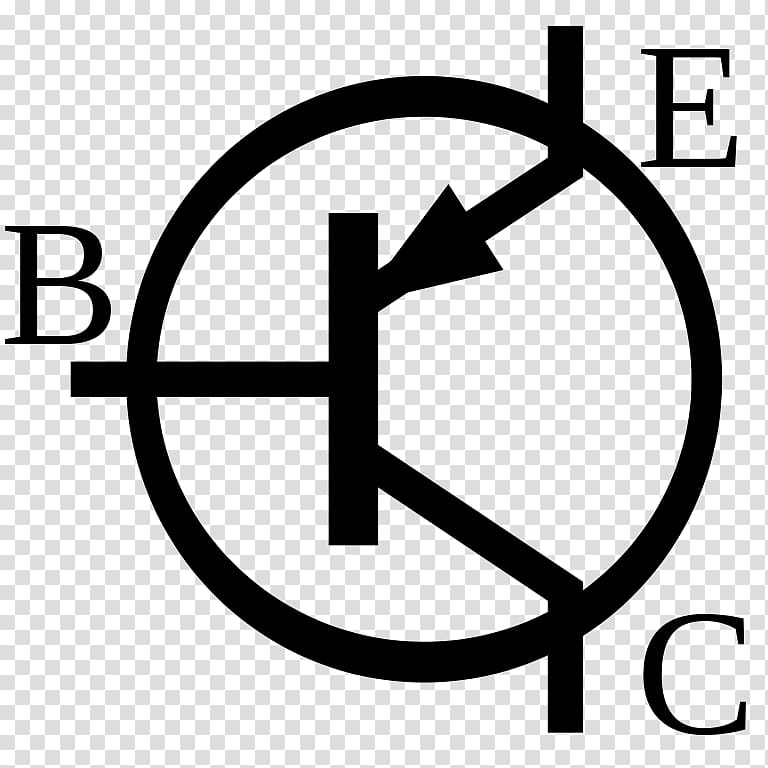
The classification of transistors can be easily understood by observing the above tree diagram. The following tree diagram explains a Basic Classification of different Transistor types. Transistor is an essential component is almost every electronic circuit like: Amplifiers, Switching, Oscillators, Voltage Regulators, Power Supplies and most importantly, the Digital Logic ICs.įrom the time of invention of the first transistor to the present day, transistors are classified into different types depending either on their construction or their operation. The Transistor is one of the important active components (a device which can produce an output signal higher power than that in the input signal). Transistors are small in size and it requires low energy for operation and also it has low power dissipation. Since a long time, the vacuum tubes are replaced with transistors because the transistors have more benefits over vacuum tubes. A Transistor is a three terminal device and a small current / voltage at one terminal (or lead) will control a large flow of current between the other two terminals (leads). Transistor is a semiconductor device which is used to either amplify the signals or to act as an electrically controlled switch. JFET (Junction-Field Effect Transistor).Transistors are an essentialĬomponent in many circuits and are sometimes used to amplify a signal. The resistor is present to protect the transistor as they can be damagedĮasily by too high a voltage / current. The transistor has to receive a voltage at its ‘ base’ and until The transistor then allows current toįlow from the +9 volts to the 0vs, and the lamp comes on. When the switch is pressed a current passes through the resistor into The circuit shown in diagram B is based on an NPN transistor. A small current or voltage at the base allows a larger voltage to flow through the other two leads When buying a transistor, directions will normally state clearly which lead is the BASE, EMITTER or COLLECTOR.ĭiagram 'A' shows an NPN transistor which is The leads on a transistor may not always be in this arrangement. The ‘tab’ on the type shown to the left is usually next to the They are notĪlways set out as shown in the diagrams to the left and right, although The diagram below shows the symbol of an NPN transistor. The EMITTER - which is the negative lead. The COLLECTOR - which is the positive lead. The BASE - which is the lead responsible for activating the transistor. Transistors are manufactured in different shapes but There are hundreds of transistors which workĪt different voltages but all of them fall into these two categories. They areĬentral to electronics and there are two main types NPN and PNP. Technology Department does not contain at least one transistor. They are used in a variety of circuitsĪnd you will find that it is rare that a circuit built in a school Transistors can be regarded as a type of switch, asĬan many electronic components.
#Transistor symbol pdf
PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE VERSION OFĬLICK HERE FOR POWERPOINT VERSION OF WORKSHEET


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
